Bridges
A bridge may be used to replace missing teeth, help maintain the shape of your face, and alleviate stress on your bite.
A bridge replaces missing teeth with artificial teeth, looks great, and literally bridges the gap where one or more teeth may have been. Your bridge can be made from gold, alloys, porcelain, or a combination of these materials and is bonded onto surrounding teeth for support.
The success of any bridge depends on its foundation — the other teeth, gums, or bone to which it is attached. Therefore, it’s very important to keep your existing teeth, gums, and jaw healthy and strong.
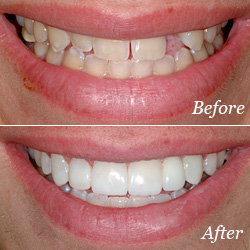
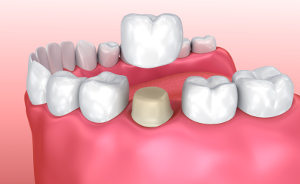
Crowns
Crowns are a restorative procedure used to improve your tooth’s shape or to strengthen a tooth. Crowns are most often used for teeth that are broken, worn, or have portions destroyed by tooth decay.
A crown is a “cap” cemented onto an existing tooth that usually covers the portion of your tooth above the gum line. In effect, the crown becomes your tooth’s new outer surface. Crowns can be made of porcelain, metal, or both. Porcelain crowns are most often preferred because they mimic the translucency of natural teeth and are very strong.
Crowns or onlays (partial crowns) are needed when there is insufficient tooth strength remaining to hold a filling. Unlike fillings, which apply the restorative material directly into your mouth, a crown is fabricated away from your mouth. Your crown is created in a lab from your unique tooth impression, which allows a dental laboratory technician to examine all aspects of your bite and jaw movements. Your crown is then sculpted just for you so that your bite and jaw movements function normally once the crown is placed.
We also offer same day crown services.
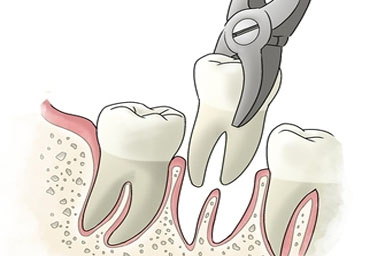
Extractions
There are times when it is necessary to remove a tooth. Sometimes a baby tooth has misshapen or long roots that prevent it from falling out as it should, and the tooth must be removed to make way for the permanent tooth to erupt. At other times, a tooth may have so much decay that it puts the surrounding teeth at risk of decay, so your doctor may recommend removal and replacement with a bridge or implant. Infection, orthodontic correction, or problems with a wisdom tooth can also require removal of a tooth.
When it is determined that a tooth needs to be removed, your dentist may extract the tooth during a regular checkup or may request another visit for this procedure. The root of each tooth is encased within your jawbone in a “tooth socket,” and your tooth is held in that socket by a ligament. In order to extract a tooth, your dentist must expand the socket and separate the tooth from the ligament holding it in place. While this procedure is typically very quick, it is important to share with your doctor any concerns or preferences for sedation.
Once a tooth has been removed, neighboring teeth may shift, causing problems with chewing or with your jaw joint function. To avoid these complications, your dentist may recommend that you replace the extracted tooth.
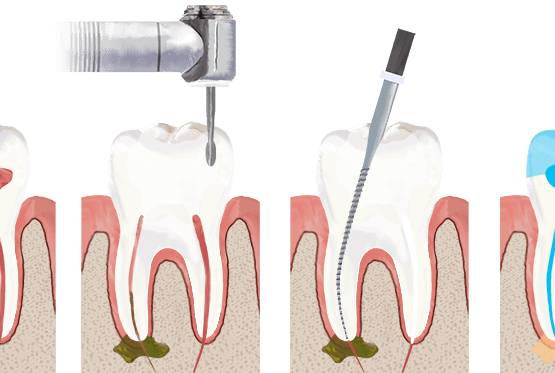
Root Canals
In the past, if you had a tooth with a diseased nerve, you'd probably lose that tooth. Today, with a special dental procedure called “root canal treatment,” your tooth can be saved. When a tooth is cracked or has a deep cavity, bacteria can enter the pulp tissue and germs can cause an infection inside the tooth. If left untreated, an abscess may form. If the infected tissue is not removed, pain and swelling can result. This can not only injure your jawbones, but it is also detrimental to your overall health.
Root canal treatment involves one to three visits. During treatment, your general dentist or endodontist (a dentist who specializes in problems with the nerves of the teeth) removes the affected tissue. Next, the interior of the tooth will be cleaned and sealed. Finally, the tooth is filled with a dental composite. If your tooth has extensive decay, your doctor may suggest placing a crown to strengthen and protect the tooth from breaking. As long as you continue to care for your teeth and gums with regular brushing, flossing, and checkups, your restored tooth can last a lifetime.
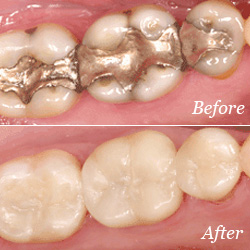
Fillings
Traditional dental restoratives, or fillings, are most often made of silver amalgam. The strength and durability of this traditional dental material makes it useful for situations where restored teeth must withstand extreme forces that result from chewing, often in the back of the mouth.
Newer dental fillings include ceramic and plastic compounds that mimic the appearance of natural teeth. These compounds, often called composite resins, are usually used on the front teeth where a natural appearance is important, but they can also be used on the back teeth depending on the location and extent of the tooth decay.
Here at the office of Dr. Steven M. Kim DDS, we provide white composite fillings to give a more natural look.